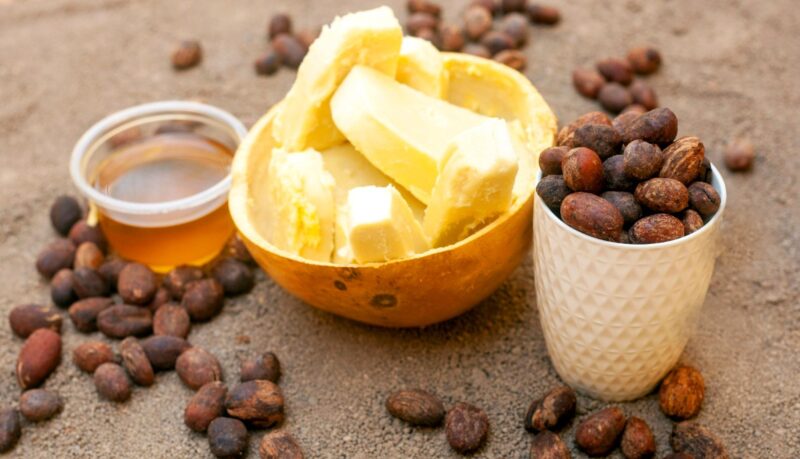
How Is Cocoa Butter Made, and Does It Fit a Vegan Lifestyle?
Cocoa butter holds a special place in kitchens, skincare routines, and health-conscious diets. Its smooth texture, mild chocolate aroma, and rich fatty acid profile have made it a common ingredient across many industries.
For readers who care about ethical sourcing and plant-based choices, the question naturally arises: How is it made, and does it fit a vegan lifestyle?
The answer involves both process and principle. Cocoa butter comes straight from cocoa beans, which are the same raw material used for chocolate. However, the steps taken to transform raw cocoa into the creamy butter often leave people curious.
Let’s explore how this unique ingredient is created, why it matters to vegans, and what to watch for in the products that include it.
Basic Characteristics

| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Source | Cocoa beans (seeds of Theobroma cacao) |
| Appearance | Pale yellow solid |
| Texture | Smooth and firm |
| Aroma | Mild, chocolatey |
| Common Uses | Skincare, chocolate, pharmaceuticals, vegan recipes |
Many confuse it with dairy butter because of the word “butter,” but the two products are entirely unrelated. Cocoa butter is completely plant-derived. Its production does not involve any animal products or by-products at any stage.
Step-by-Step Guide
1. Harvesting the Cocoa Pods
The production begins in tropical regions. Farmers harvest ripe cocoa pods by hand. Each pod contains 30 to 50 seeds surrounded by sweet pulp.
2. Fermentation of Cocoa Beans
After collection, the beans and pulp are removed and placed in shallow boxes or banana leaves. They undergo fermentation for five to seven days. This step improves flavor and texture.
3. Drying the Beans
Fermented beans are then dried under the sun. Proper drying prevents mold and spoilage. This phase can last a week or more depending on the climate.
4. Roasting
Once dried, the beans are roasted at specific temperatures. Roasting enhances the chocolatey aroma and kills microbes. The outer shell becomes brittle and separates easily.
5. Cracking and Winnowing
Roasted beans are cracked to remove their outer shells. What remains is called a cocoa nib. These nibs are the essence of the cocoa flavor and the source of cocoa butter.
6. Grinding the Nibs
The nibs are ground into a thick paste called cocoa liquor. Despite the name, cocoa liquor contains no alcohol. It consists of both cocoa solids and cocoa fat in liquid form.
7. Pressing the Cocoa Liquor
Cocoa liquor is then placed in hydraulic presses. Pressure separates the cocoa solids from the fat. The fat portion is collected and cooled to become cocoa butter.
8. Filtering and Purifying
Some manufacturers filter the cocoa butter to remove residual particles. Others leave it in a more raw form for natural or organic markets.

Is it Vegan?
Cocoa butter qualifies as vegan by definition. It comes entirely from the cacao plant. No animals, animal by-products, or animal-derived enzymes play any role in its production.
Why the Name Causes Confusion
The term “butter” often leads people to associate it with dairy. However, cocoa butter does not come from milk or any animal source. It is simply a plant fat with a creamy consistency, much like shea butter or mango butter.
What Makes It Vegan-Friendly?
- 100% plant origin
- No animal processing
- Compatible with dairy-free, egg-free diets
Certified vegan products containing cocoa butter must also exclude milk solids, whey, or lecithin derived from eggs or animal sources. Always verify the ingredient list.
Where You Will Find Cocoa Butter
It appears in a wide range of products. While the base ingredient is vegan, its final use can vary depending on the manufacturer.

Common Products
| Category | Product Examples |
|---|---|
| Food | Dark chocolate, dairy-free spreads, baking bars |
| Skincare | Lip balm, lotions, moisturizers, soaps |
| Pharmaceuticals | Capsules, ointments |
| Haircare | Conditioners, styling creams |
Vegans who care about cruelty-free and plant-based living often encounter cocoa butter in chocolate. However, chocolate can also contain milk powder, honey, or non-vegan emulsifiers. Always look for certified vegan labels.
Cocoa Butter vs. Other Plant Butters
Many confuse cocoa butter with similar-sounding alternatives. Knowing the distinctions helps make better buying decisions.
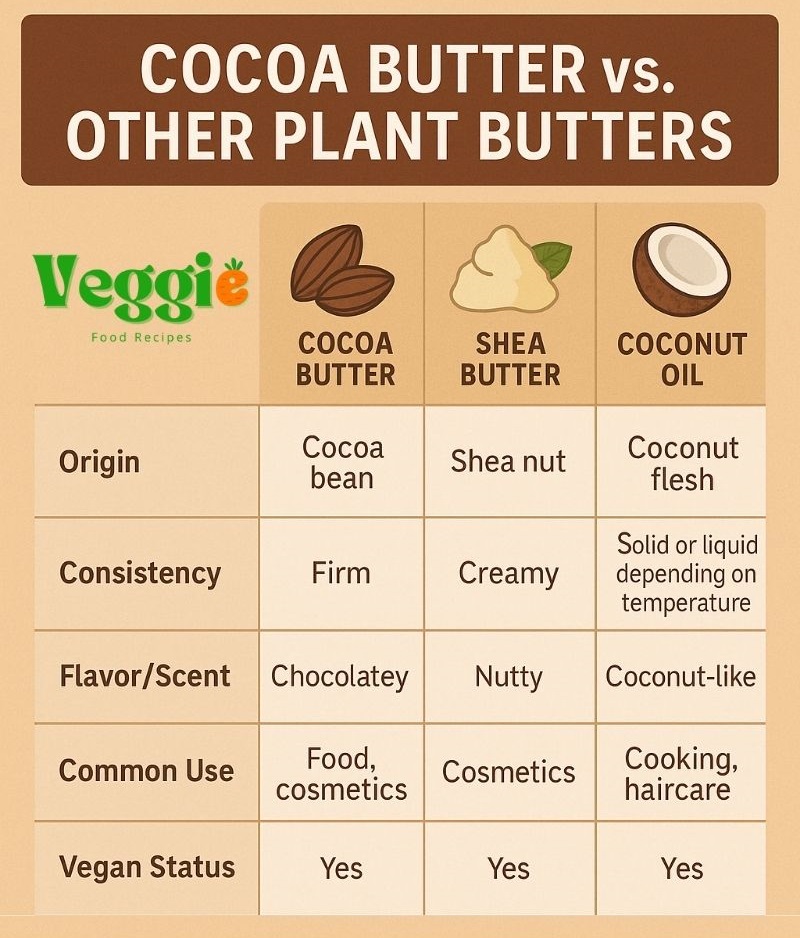
Comparison Table
| Feature | Cocoa Butter | Shea Butter | Coconut Oil |
|---|---|---|---|
| Origin | Cocoa bean | Shea nut | Coconut flesh |
| Consistency | Firm | Creamy | Solid or liquid depending on temperature |
| Flavor/Scent | Chocolatey | Nutty | Coconut-like |
| Common Use | Food, cosmetics | Cosmetics | Cooking, haircare |
| Vegan Status | Yes | Yes | Yes |
All three options serve different roles. Cocoa butter remains the preferred choice for chocolate, confections, and firm skincare products.
Use in Vegan Diet
Plant-based chefs love cocoa butter for its silky texture and mild flavor. It appears in raw vegan recipes, chocolate making, and even vegan butter alternatives.
Ways to Use it in Vegan Recipes
- Chocolate truffles with maple syrup and vanilla
- Dairy-free white chocolate
- Plant-based fudge
- Smoothies with cacao and fruit
- Vegan fat bombs for keto diets
Melting and blending it with other plant fats like coconut oil allows for endless creative options in vegan cooking.
Shelf Life and Storage
Cocoa butter has a long shelf life due to its stable fat content. It can last two to five years if stored properly.
Storage Tips
- Keep in a cool, dry place
- Avoid direct sunlight
- Use airtight containers
- Do not store near strong odors
Its high oxidative stability means you will rarely encounter rancid cocoa butter. That makes it an ideal pantry or skincare staple.
What to Watch for in Labels
Although the butter itself is vegan, many processed goods include additives that do not meet vegan standards. Labels often include terms that need attention.
Common Ingredients to Verify
| Ingredient | Vegan? | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Milk powder | No | Common in commercial chocolate |
| Lecithin | Sometimes | Soy lecithin is vegan, egg lecithin is not |
| Glycerin | Sometimes | Can be plant-based or animal-based |
| Natural flavors | Depends | Source not always disclosed |
| Whey | No | Dairy by-product |
| Honey | No | Derived from bees |
Look for “certified vegan” logos and read full ingredient lists.
Final Thoughts
Cocoa butter qualifies as vegan by all ingredient standards. It originates from cocoa beans without any contact with animal products during harvesting, processing, or production. Its smooth texture and versatility make it a favorite among plant-based food makers and cruelty-free skincare brands.
Vegan readers should remain cautious when checking product labels. Many companies blend cocoa butter with dairy, egg-derived emulsifiers, or hidden animal ingredients. When used on its own or paired with other plant-based ingredients, cocoa butter supports a cruelty-free lifestyle.
The next time you enjoy a chocolate bar or apply a soothing balm, remember that cocoa butter brings both comfort and clarity. It proves that plant-based choices can feel luxurious, ethical, and delicious at the same time.
Hello, my name is Marina Vlasov. Im currently trying to change my career from my current job to becoming a chef. It is a hard road, but I feel like im coming there soon. While I enjoy preparing practically all food, from various cuisines from all over the globe, I must say that I mostly enjoy preparing vegan food. That is my strongest side. That is why I want to provide you with the best vegan food recipes on this blog of mine.

